Hi Python programmers, In this guide, we are going to learn how to convert SQL Query Result to Pandas DataFrame. Here we will use one of the most popular Python packages Pandas, In our previous tutorials, we have already covered. Throughout this guide, we will use the MySQL database.
Most of the time as a developer you need to convert SQL query to Pandas DataFrame, Then we have the best package pandas that provide a read_sql() function to deal with SQL queries. To convert SQL query to pandas DataFrame first of all you have to establish a connection from MySQL server using SQLAlechemy.
Prerequisites
To convert SQL query to the database you have to install these two python packages using the pip command.
pip install pandas
pip install sqlalchemyHeadings of Contents
Steps to convert SQL query to DataFrame
Here are some steps listed that are required to convert SQL query results to Pandas DataFrame.
- Make sure you have already created a MySQL Database and table, otherwise, you can follow this article.
- Import Pandas and create_engine from SQLAlchemy.
- Make a MySQL connection string using the create_engine() function.
- Pass database connection and SQL query to pandas read_sql() function to convert SQL to DataFrame in Python.
Establish MySQL Connection
To make a MySQL connection we should have the following credentials. As you can see in the below screenshot.
You have to replace it with your credentials.
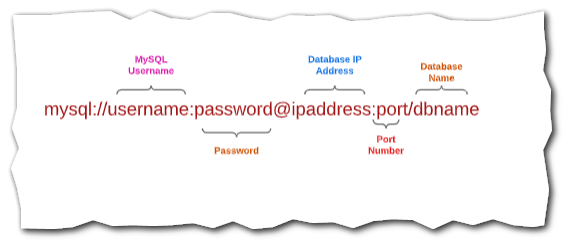
- host or IP address
- user
- password
- port
- database name
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
mydb = create_engine('mysql://root:root21@localhost:3308/testing')As you can see, we have established a MySQL connection.
Note:- In your case, all the credentials might be different.
In demodb database, we have a table called students which contains the following records.
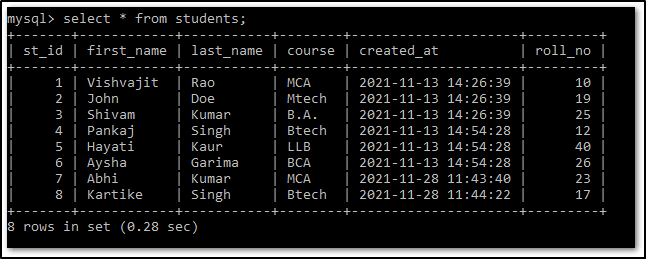
Convert SQL Query Result to Pandas DataFrame
After creating the MySQL connection string, we have to write an SQL query that selects the records from the table. Pass SQL query and MySQL connection string into read_sql() method.
Example
import pandas as pd
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
# connection build
mydb = create_engine('mysql://root:root21@localhost:3308/testing')
# sql query
query = 'SELECT * FROM students'
# convert sql query to dataframe
df = pd.read_sql(query, mydb)
# print dataframe
print(df)Output
st_id first_name last_name course created_at roll_no
0 1 Vishvajit Rao MCA 2021-11-13 14:26:39 10
1 2 John Doe Mtech 2021-11-13 14:26:39 19
2 3 Shivam Kumar B.A. 2021-11-13 14:26:39 25
3 4 Pankaj Singh Btech 2021-11-13 14:54:28 12
4 5 Hayati Kaur LLB 2021-11-13 14:54:28 40
5 6 Aysha Garima BCA 2021-11-13 14:54:28 26
6 7 Abhi Kumar MCA 2021-11-28 11:43:40 23
7 8 Kartike Singh Btech 2021-11-28 11:44:22 17Select records with condition
Sometimes we need to select and convert into DataFrame only those records that follow specific conditions. Let’s see how can we do that.
Example
import pandas as pd
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
# connection build
mydb = create_engine('mysql://root:root21@localhost:3308/testing')
# sql query
query = 'SELECT * FROM students WHERE roll_no >= 10 AND roll_no <= 20'
# convert sql query to dataframe
df = pd.read_sql(query, mydb)
# print dataframe
print(df)In the above example, we have just selected only those students records whose roll_no is greater than or equal to 10 and less than or equal to 20. As you can see below output.
Output
st_id first_name last_name course created_at roll_no
0 1 Vishvajit Rao MCA 2021-11-13 14:26:39 10
1 2 John Doe Mtech 2021-11-13 14:26:39 19
2 4 Pankaj Singh Btech 2021-11-13 14:54:28 12
3 8 Kartike Singh Btech 2021-11-28 11:44:22 17Select a specific number of rows
As you can see in all the above examples, we did not restrict, how many numbers of rows should be returned, it will always return all the possible rows but sometimes we want to return only a specific number of rows. To do that we have two possible ways using the DataFrame head() method and passing chunksize in the read_sql() method.
Using Head() method
DataFrame head() method takes a number that represents several records that should be returned.
Example
import pandas as pd
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
# connection build
mydb = create_engine('mysql://root:root21@localhost:3308/testing')
# sql query
query = 'SELECT * FROM students'
# convert sql query to dataframe
df = pd.read_sql(query, mydb)
# print only rows
print(df.head(5))Output
st_id first_name last_name course created_at roll_no
0 1 Vishvajit Rao MCA 2021-11-13 14:26:39 10
1 2 John Doe Mtech 2021-11-13 14:26:39 19
2 3 Shivam Kumar B.A. 2021-11-13 14:26:39 25
3 4 Pankaj Singh Btech 2021-11-13 14:54:28 12
4 5 Hayati Kaur LLB 2021-11-13 14:54:28 40Using chunksize Parameter
The read_sql() method chunk size parameter is also capable of returning a specific number of records that takes an integer value.
Example
import pandas as pd
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
dataframes = []
# connection build
mydb = create_engine('mysql://root:root21@localhost:3308/testing')
# sql query
query = 'SELECT * FROM students'
# convert sql query to dataframe
chunks = pd.read_sql(query, mydb, chunksize=5)
for chunk in chunks:
dataframes.append(chunk)
df = pd.concat(dataframes)
print(df)
Output
st_id first_name last_name course created_at roll_no
0 1 Vishvajit Rao MCA 2021-11-13 14:26:39 10
1 2 John Doe Mtech 2021-11-13 14:26:39 19
2 3 Shivam Kumar B.A. 2021-11-13 14:26:39 25
3 4 Pankaj Singh Btech 2021-11-13 14:54:28 12
4 5 Hayati Kaur LLB 2021-11-13 14:54:28 40
0 6 Aysha Garima BCA 2021-11-13 14:54:28 26
1 7 Abhi Kumar MCA 2021-11-28 11:43:40 23
2 8 Kartike Singh Btech 2021-11-28 11:44:22 17Conclusion
So, In this guide, we have seen all about how to convert SQL Query Result to Pandas DataFrame.This is one of the legit approaches to convert any SQL query result DataFrame using Python. Make sure you have downloaded Pandas and SQLAlchemy in your system using the pip command.
I hope this article will help you. if you like this article, please share and keep visiting for further Python interesting tutorials.
Related Articles:-
Thanks for your valuable time ….